fixedd digital
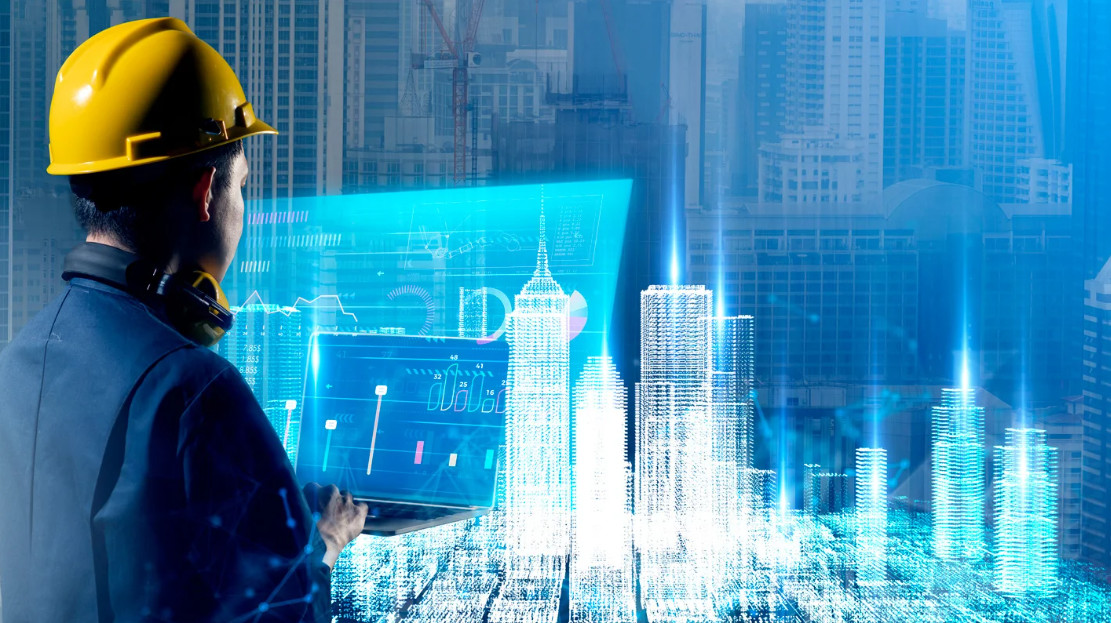

In recent decades, Building Information Modelling (BIM) has emerged as a transformative force in the construction sector. BIM empowers architects, engineers, and builders to create detailed virtual models of buildings, streamlining planning, design, and construction processes. However, while BIM remains indispensable, it represents just the tip of the iceberg in the realm of digital construction.
The construction industry is experiencing a seismic shift towards digitalisation, driven by an array of cutting-edge technologies. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are revolutionising the way architects and builders visualise and interact with their designs. VR enables immersive walkthroughs of virtual constructions, allowing stakeholders to experience spaces before they’re built, while AR overlays digital information onto the physical environment, enhancing on-site decision-making.
Moreover, the advent of the Building Internet of Things (BIoT) is ushering in a new era of smart buildings. BIoT integrates Internet of Things (IoT) technology with building systems, enabling real-time monitoring, control, and optimisation of building operations. From energy management to occupant comfort, BIoT-driven solutions enhance building performance and sustainability, paving the way for a more efficient and responsive built environment.
Furthermore, cloud computing has emerged as a catalyst for collaboration and data management in construction projects. Cloud-based platforms facilitate seamless sharing of project information among stakeholders, enabling real-time communication, document management, and version control. This level of connectivity fosters greater transparency, efficiency, and accountability throughout the project lifecycle, particularly in complex, multi-disciplinary endeavours.
In essence, while BIM continues to underpin digital transformation in construction, the industry’s evolution extends far beyond it. The convergence of VR, AR, BIoT, and cloud computing represents a paradigm shift in how buildings are conceived, constructed, and operated. As these technologies continue to mature and converge, they promise to unlock new possibilities for innovation, sustainability, and resilience in the built environment. The future of construction is digital, and it’s an exhilarating journey of exploration and advancement for industry professionals worldwide.
The Birth of BIM:
Building Information Modeling (BIM) emerged as a response to the limitations of traditional 2D CAD systems. In the late 20th century, architects, engineers, and construction professionals sought a more collaborative and efficient approach to building design and construction. The concept of BIM began to take shape in the 1990s, with pioneers like Charles M. Eastman and the work at the Georgia Institute of Technology’s Digital Building Laboratory laying the foundation.

By the early 2000s, BIM software started to gain traction, offering a three-dimensional digital representation of buildings and infrastructure. This shift allowed stakeholders to visualize projects more comprehensively, enabling better coordination, clash detection, and cost estimation throughout the lifecycle of a building.
The Rise of IoT:
The Internet of Things (IoT) evolved from the convergence of various technologies, including wireless communication, sensors, and embedded systems. While the concept of connecting devices and machines to the internet dates back to the late 20th century, the term “Internet of Things” gained prominence in the early 2000s.
Advancements in microelectronics, cloud computing, and data analytics accelerated the adoption of IoT across industries. In the context of the built environment, IoT enables the integration of sensors and smart devices into buildings and infrastructure, facilitating real-time monitoring, automation, and optimization of energy usage, occupancy, and maintenance.
The Advent of AI:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) traces its roots to the mid-20th century, with early developments in machine learning, neural networks, and expert systems. However, it wasn’t until the 21st century that AI experienced significant advancements, driven by improvements in computational power, algorithms, and data availability.

Today, AI permeates various aspects of society, including the AEC and MFG industries. In construction, AI-powered solutions offer capabilities such as predictive analytics, generative design, and autonomous construction equipment. These technologies promise to revolutionize project planning, design optimization, and operational efficiency.
The Future of the Trinity:
Looking ahead, the integration of BIM, IoT, and AI is poised to reshape the future of the built environment profoundly. Together, these technologies enable the creation of “smart” buildings and infrastructure that are not only more efficient and sustainable but also safer and more responsive to occupants’ needs.
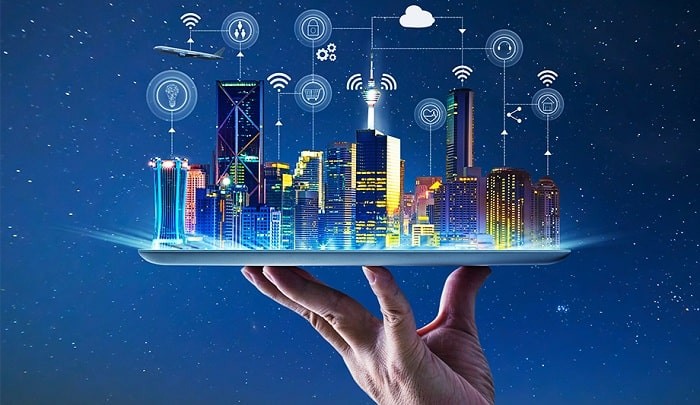

In the coming years, we can expect to see further convergence and synergies among BIM, IoT, and AI, leading to more intelligent and interconnected built environments. From enhanced design workflows to predictive maintenance and resilient infrastructure, the trinity of BIM, IoT, and AI holds the potential to drive unprecedented innovation and transformation in the AEC and MFG industries.

